Photo: CCTV News
China has successfully established the world's first three-satellite constellation on the distant retrograde orbit (DRO) in the Earth-moon region of space, connecting them with stable inter-satellite measurement and communication links, Global Times learned from program developer the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
Such development has yielded variety of original scientific and technology outcomes, laying a solid ground for the country's future development of the Earth-moon region of space and frontier exploration of the space science, the CAS disclosed in the statement it provided to the Global Times on Wednesday.
Per the CAS, the Earth-moon region of space refers to the expanded domain extending outward from Earth's orbit, reaching up to 2 million kilometers from Earth. Compared to Earth's orbital space, its three-dimensional volume expands by more than a thousand times, the academy explained.
Developing and utilizing cislunar space holds tremendous strategic significance for lunar resource exploitation, long-term human habitation beyond Earth, interplanetary activities, and the sustainable exploration of the solar system, it added.
The CAS launched preliminary research and key technology development in this region in 2017. In February 2022, a pilot project was initiated to develop and launch three satellites to form a large-scale satellite constellation in the region of space, aimed at exploring the unique characteristics and application potential of the DRO.
The DRO-A and -B satellites were launched in March 2024, and entered their mission orbit on July 15 the same year, while the DRO-L was launched in February 2024 into a sun-synchronous orbit and began conducting experiments as planned. The three formed the constellation for the first time in August 2024.
The plan included DRO-A satellite permanently staying in the DRO, while the DRO-B satellite operates in Earth-moon space maneuver orbits, according to CAS' Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization (CSU.)
Chinese scientists have made significant breakthroughs in ranging fields since the set-up of the three-satellite constellation in 2024.
Building on years of research in Earth-moon region of space astrodynamics and space exploration, the scientific team proposed an innovative design concept: trading longer flight time for increased payload capacity and greater contingency margin. As a result, the satellites completed Earth-moon transfer and achieved low-energy DRO insertion using only one-fifth of the fuel required by traditional methods, marking the world's first successful low-energy insertion into a DRO.
This breakthrough significantly reduces the cost of accessing cislunar space, opening up new avenues for large-scale development and utilization.
The team also achieved another world-first by successfully verifying a 1.17-million-kilometer K-band inter-satellite microwave measurement and communication link, overcoming a major technological bottleneck in building large-scale constellations in cislunar space.
In terms of space science, the mission has also supported astrophysical research such as gamma-ray burst detection and trialed new technologies, including operating atomic clocks.
Moreover, Chinese researchers successfully validated a new space-based orbit determination system whereby one satellite tracks another, replacing traditional ground-based tracking. Using just three hours of inter-satellite measurement data, they achieved orbit determination accuracy equivalent to over two days of traditional ground tracking. This breakthrough significantly lowers the cost of orbit determination for cislunar spacecraft, paving the way for more efficient operations.
Wang Wenbin, a researcher at CSU, hailed that this achievement marks the first time internationally that orbit determination was verified using satellite-to-satellite tracking rather than ground stations.
"It's like turning a traditional ground station into a satellite and placing it in a low-Earth orbit," he explained. "This opens a new technical pathway for China's future cislunar and deep space exploration. It also provides an efficient solution for orbit determination, navigation, and timing across various cislunar orbits, supporting the future expansion of large-scale commercial activity in cislunar space."
Researchers told the Global Times on Wednesday that the program would support China's future lunar exploration mission, including providing space-based inter-satellite measurement for rapid orbit determination and autonomous navigation services for lunar exploration mission orbiters, and supply high-precision time signals for lunar surface facilities.
Additionally, as the DRO is far from Earth and the moon, free from obstructions, it could facilitate the establishment of communication links with lunar exploration mission spacecraft, and assist in the downlink of critical or emergency data, researchers explained.
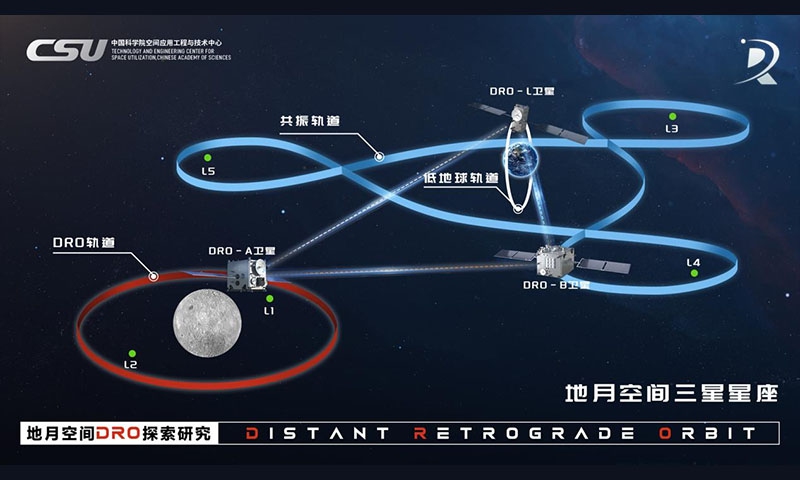
A diagram of the world's first three-satellite constellation on the distant retrograde orbit (DRO) in the Earth-moon region established by China Photo: Courtesy of the Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization, Chinese Academy of Sciences
China has successfully established the world's first three-satellite constellation on the distant retrograde orbit (DRO) in the Earth-moon region of space, with the constellation operating stably for over 200 days, the Global Times learned at an academic seminar held by the project's developer, the Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization (CSU) at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently.
Apart from sharing this groundbreaking achievement, a particular detail discussed at the seminar attracted widespread attention: During the launch of two satellites in the three-satellite constellation - DRO-A and DRO-B - in March 2024, the mission once encountered anomalies. However, the situation was successfully navigated, under the 123-day dedicated efforts by the project's team at the center, with an average age of under 34.
What thrilling events unfolded during the rescue of the malfunctioning satellites, which were tens of thousands of kilometers away? What challenges did the program's team face and overcome? What significance does this launch hold for China's space endeavors and the development of humanity? The Global Times recently spoke with two participants from the project, who recounted how this young team turned a potential space disaster into a success.
Anomaly in satellite launch
In mid-April, the CSU released images of a DRO-A satellite with its solar panel severely damaged.
The satellite, which is still operational, evokes Zhang Hao's memories of March 13, 2024. That evening, at 8:51 pm, China launched the DRO-A/B satellites using the Long March-2C carrier rocket with a Yuanzheng-1S (Expedition-1S) upper stage attached, from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center. It was a historic moment, marking China's first foray into the deep exploration of the DRO.
The DRO is a unique family of orbits between the Earth and the moon. A typical DRO is located around 310,000 to 450,000 kilometers from the Earth, or 70,000 to 100,000 kilometers from the moon. Compared to other orbits, the DRO offers greater stability, allowing spacecraft to remain in position for hundreds of years without frequent adjustments. It is regarded by the aerospace community as a "natural harbor in the Earth-moon space." Following the launch of the DRO-A/B satellites, they are expected to work in conjunction with the previously launched DRO-L satellite, to establish K-band microwave inter-satellite measurement and communication links.
"Together, they will form a lighthouse or a beacon for further deep space exploration by us," Zhang, a research fellow at the CSU, told the Global Times.
However, shortly after the launch that evening, news of an "anomaly during the DRO-A/B satellite launch" drew public attention: While the first and second stages of the rocket flew normally, the upper stage, which is directly responsible for placing the satellites in their designated orbit, experienced an anomaly, resulting in the satellites not reaching their intended trajectory.
Zhang, responsible for orbital design and mission planning in this project, recalled details from that moment in the mission control center. At about 11 pm, signaling the imminent separation of the satellites from the rocket, the parameters representing the apogee height on the large screen suddenly fluctuated violently: The apogee height, which was supposed to steadily increase to 292,000 kilometers, instead oscillated like a roller coaster at just 150,000 kilometers.
Yin Yongchen, a third-year doctoral student at the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS), is one of the Gen Z members of the project team. That night, the 24-year-old, who was busy with the relevant Ground System and was not directly aware of the situation on-site, recalled that several dozen minutes had passed beyond the expected time of the separation [of the satellites from the rocket] without any updates.
"I felt a vague sense of unease," he said. As midnight approached, Yin received a message from Zhang informing him that there was indeed a problem with the launch. "My heart sank at that moment."
In this project, Yin's role primarily involved assisting Zhang with contingency planning prior to the satellite launch. Now that an emergency had truly arisen, he realized that their upcoming tasks would be even more challenging.
Finally, after approximately 40 minutes of losing contact, the Telemetry, Tracking, and Command (TT&C) system captured a flickering signal. The team discovered that the DRO-A/B satellite duo had been "thrown" into an orbit at an apogee of only 134,000 kilometers - far below the intended 292,000 kilometers.
Worse still, it was spinning at over 200 degrees per second at that time.
"If these satellites did not regain their status within a few hours, their power may run out, or if they continued spinning at such high speeds, they would fall apart, become multiple pieces of space debris," Zhang told the Global Times.
"We needed to quickly and efficiently find a solution and implement it before that happened," Zhang said.

Aero-engineers work at the Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization (CSU), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), on January 18, 2024. Photos on this page: Courtesy of the CSU
Youth power
The project team made multiple adjustments to the trajectory of the DRO-A/B satellite constellation in the following months. This "space rescue" was officially declared a success on July 15, 2024, lasting 123 days. Later, on August 28, DRO-A and DRO-B were successfully separated.
The project team accomplished this remarkable feat, covering approximately 8.5 million kilometers, while consuming only one fifth of the fuel typically required for such missions. The space rescue not only salvaged satellites, but also validated several "world firsts," such as low-energy transfer for the DRO spacecraft, inter-satellite communication over a distance of 1.17 million kilometers, and a new system for space-based orbit determination.
Zhang, who participated in the satellite launch control process for the first time, reflected on the valuable experience he gained during the mission. "In this rescue, we collaborated closely with people from different institutions, and I accumulated a lot of practical experience," he said. "More importantly, the successful orbital insertion of the satellite is only a beginning, subsequent on-orbit technical breakthrough and scientific discoveries are waiting ahead of us."
According to Zhang, the three-satellite constellation, which includes DRO-A, DRO-B, and the previously launched DRO-L, is expected to serve as a guiding beacon and communication hub for future space navigation. It can also function as space laboratories due to its unique gravitational field. Moreover, in the future, the constellation may serve as infrastructure for lunar resource development, and even pave the way for information highways for Mars exploration.
Despite the significance of the mission, the team executing it is remarkably young. A millennial himself, Zhang noted that most team members are millennials. He praised the Gen-Z students involved in the project for their strong technical skills, sense of responsibility, and passion for aerospace research. "The system of integrating research and education of UCAS, or more broadly, our national education system, has laid the foundation for the Gen-Z students to deal with these situations".
Yin recalled the overwhelming sense of achievement and joy he felt when the rescue was officially declared successful. "As a student, being part of this rescue and witnessing this historic moment in China's space history, is something I take great pride in," he told the Global Times.
May 4 marks China's Youth Day. Yin said that there are more and more young people like him who are proud of China's great achievements in space exploration, with a dream of embarking on a journey "to the sea of stars," by joining the aerospace industry. "It is truly an honor for our younger generation to witness, and even contribute to, China's rise as a space power," he said.
Get through challenges
An emergency rescue effort on the ground was mounted. Challenges came one after another.
The first challenge was to stop the spinning 581-kilogram DRO-A/B satellite duo. The project team repeatedly uploaded contingency commands, modifying parameter thresholds, alternately using the engines of each satellite to eliminate the spinning. In an attempt to "talk" to the satellites, the flight control team had to issue each command multiple times. By around 3 am the next day, the satellite duo successfully ceased its high-speed spinning.
Next came the second challenge. Telemetry data indicated that the solar panel of the DRO-A satellite could not lock, while the solar panel of the DRO-B satellite was completely "dislocated." As the power source for the satellites, any anomaly with the solar panels could lead to a critical power shortage, risking total energy depletion.
The team urgently implemented a series of operations, including uploading attitude control commands, and repeatedly adjusting the sun-pointing attitude. At last, they managed to successfully "recharge" the satellite with the damaged solar panels.
Having overcome these two major challenges, the real test was just beginning. At the time, the apogee altitude of the DRO-A/B satellites was less than half of what was expected, and fuel reserves were critically low.
How could the satellites be brought back on track? Within 40 hours, the team members engaged in heated discussions, scribbling formulas, coding, and repeatedly calculating a plan to return the satellites to their intended orbit amid the complex influences of various gravitational forces. During this period, Zhang and some colleagues hardly rested. "I was highly tense and concentrated, and didn't even feel tired," said Zhang.
Majoring in Astrodynamics, Yin participated in the review of orbital control parameters during this rescue. The task required meticulousness and patience. Yin recalled that each review of the orbital control parameters was time-sensitive, necessitating timely command uploads to the satellites.
Under pressure, Yin made a slight error in setting the engine parameters, which delayed the successful review of the parameters. "I was quite anxious at that moment, worried that my mistake would hinder the normal execution of the mission," he told the Global Times. The issue was later promptly identified and resolved with the help of the team's veteran members.
Time passed during the tense yet orderly rescue operation. At 12:42 pm on March 18, 2024, nearly five days after launching the first contingency orbital control maneuver, the apogee altitude of the satellites was successfully raised to the intended height of about 240,000 kilometers, bringing a sigh of temporary relief to the entire team. A few days later, the project team conducted a second perigee orbital maneuver, successfully elevating the combination to around 380,000 kilometers.
Reflecting on the process of overcoming each challenge with his coworkers, Zhang described their overall demeanor as "busy yet composed." He mentioned that before satellite launching, they would brainstorm in advance about potential malfunctions, and prepare relevant countermeasures.