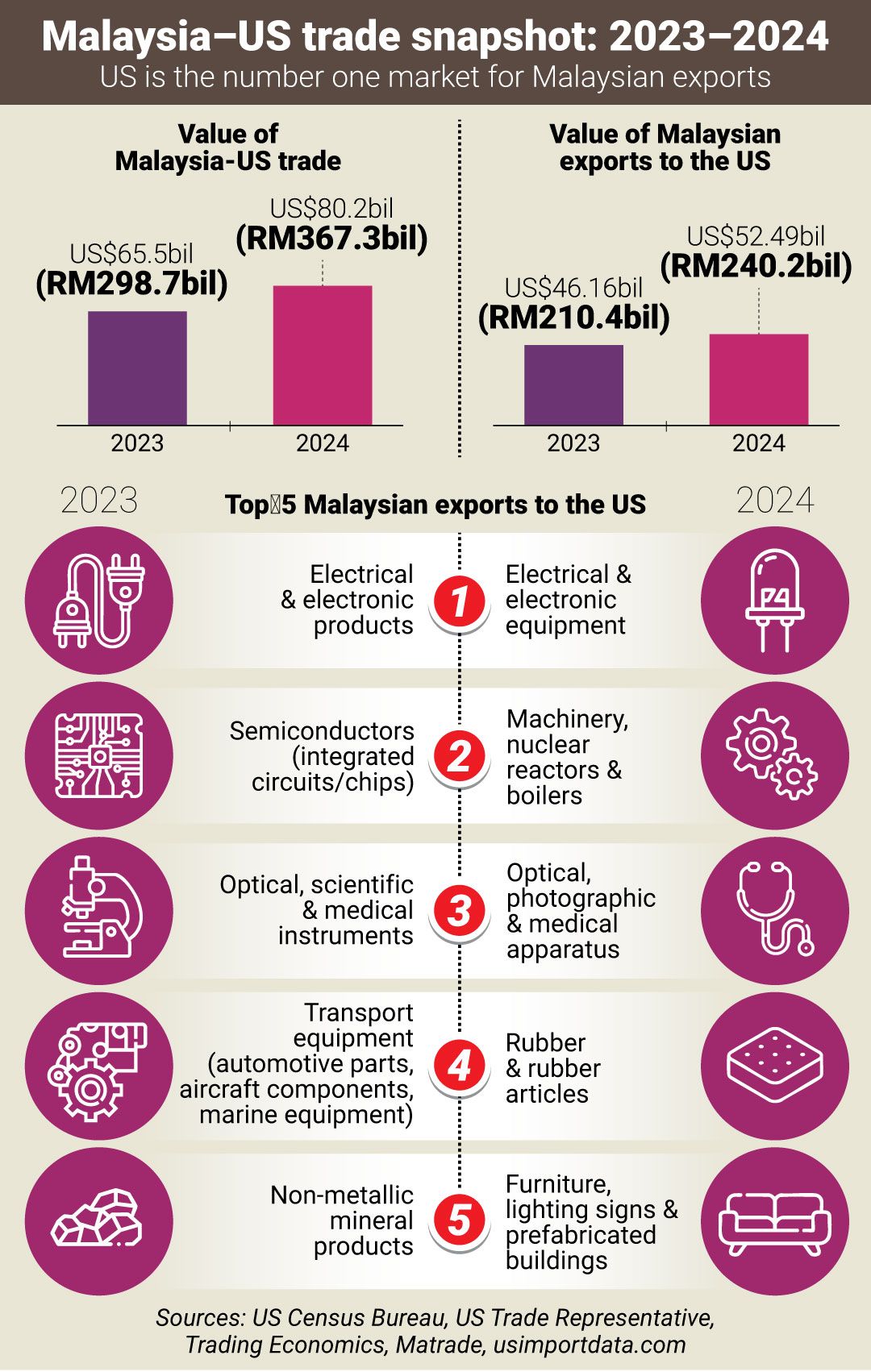
However, nation must urgently diversify its export destinations
PETALING JAYA: Malaysia’s revised tariff rate of 19% on exports to the United States offers a temporary competitive edge in the region but underscores the urgency for export diversification amid signs of growing US protectionism, economists warn.
Prof Emeritus Dr Barjoyai Bardai said the revised rate, down from 25% previously, positions Malaysia on par with neighbouring countries such as Thailand, Indonesia, Cambodia and the Philippines.
ALSO READ: Malaysian industries can breathe easier now
He said the rate is still more favourable than those imposed on Myanmar (40%), Vietnam (20%) and Taiwan (20%).
“We seem to be able to compete with our neighbouring countries. But we are far behind Singapore at 10%, as well as Japan and South Korea at 15%.
“With India at 25%, we are in a better position,” he said when contacted. What we really want to see is that the tariff imposed on Malaysia is as low or better than that of countries that are our competitors because we are exporting to the United States.
“So, if those countries have equal or higher tariffs than us, then our ability to compete remains intact,” he added.
However, he said that certain Malaysian exports may be vulnerable, especially low-margin products such as solar panels, and electrical and electronic goods.
On the trade balance with the US, he said it depends on whether Malaysian imports from the US increase significantly, especially luxury goods, following the government’s decision to scrap the luxury tax.
“Although the luxury tax has been included in the expanded SST, the rate is still low,” he added.
He said Malaysia must urgently diversify its export destinations, as the US moves towards a more self-sufficient economy.
Barjoyai said semiconductors should be directed to countries with growing demand, such as China, India and Europe.
For other items like solar panels, he said Malaysia should consider Latin America, Canada and Europe.
“There are still many untapped markets. In the long run, the United States will become a domestic-driven economy where they will seek to reduce imports.
“Today, they are already about 80% self-sustaining,” he added.
Echoing similar concerns, Bank Muamalat Malaysia Bhd chief economist Dr Mohd Afzanizam Abdul Rashid said the tariff adjustment signals that the United States remains open to dialogue, but the economic implications for Malaysia remain.
“As a result of recent discussions, the previously imposed retaliatory tariffs of 25% have now been reduced to 19%.
“Consequently, the negative impact on Malaysia’s economy is expected to be slightly mitigated.
“In this regard, Bank Negara has revised its GDP forecast for 2025 to a range of 4.0% to 4.8%, down from the earlier projection of 4.5% to 5.5%,” he said.
Afzanizam also highlighted the potential global impact of US tariffs.
“The 19% import tariff is expected to impact American consumers’ purchasing power.
“This may, in turn, dampen economic momentum in the US, which is the world’s largest economy. It poses a potential risk to global economic growth in the coming years,” Afzanizam said.
He also called for a balanced approach to foreign relations and economic strategy.
“It is crucial to preserve strong bilateral ties with the United States, while simultaneously exploring new opportunities with countries in Europe, the BRICS bloc, and strengthening economic and diplomatic cooperation within Asean.
“At the same time, efforts to boost productivity, build capacity and enhance economic resilience must be intensified to safeguard Malaysia’s economic sovereignty.
“These measures will reinforce investor and business confidence, underpinned by pragmatic policies and the government’s proactive response to emerging challenges,” he added.
Centre for Market Education chief executive officer Carmelo Ferlito, meanwhile, said the tariff revision reflects a political strategy rather than a pure economic measure.
“The reciprocal tariff on Malaysia to 19% is the proof of what I have mentioned earlier,” he said, adding that US President Donald Trump was not interested in tariffs per se, but to reopen negotiating tables.
He said this is to show that the United States is the biggest consumer in the world and force countries to get closer to the United States as well as grant commercial facilitations.
Ferlito criticised the use of tariffs as a policy tool, arguing that they hurt both consumers and workers.
“Tariffs are bad, not just for Malaysia, but for the world,” he said, adding that ultimately, tariffs reduce trade opportunities.
“This means less choice for consumers, but also job losses, on both sides,” he added.